-
백준 17070, 2212, 12018, 14719Java/코딩테스트 2023. 7. 26. 17:04
백준 17070
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/17070
17070번: 파이프 옮기기 1
유현이가 새 집으로 이사했다. 새 집의 크기는 N×N의 격자판으로 나타낼 수 있고, 1×1크기의 정사각형 칸으로 나누어져 있다. 각각의 칸은 (r, c)로 나타낼 수 있다. 여기서 r은 행의 번호, c는 열의
www.acmicpc.net
- BFS로도 풀어보고, DP로도 풀어봤다. 처음에 BFS풀 때 움직일 수 있는 모든 방향을 리스트에 저장해서 다 도는 방식으로 구현했었는데, 시간초과 났었다.
- 오른쪽으로 이동 가능한 경우 : 이전이 대각선이거나 가로 방향일 때
- 아래로 이동 가능한 경우 : 이전이 대각선이거나 세로 방향일 때
- 대각선으로 이동 가능한 경우 : 이전 상태 상관없이 다 가능
이렇게 3가지 케이스로 나눠서 풀어야 한다.import java.util.*; import java.io.*; public class p17070_BFS { private static int n, answer = 0; private static int[][] map; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); map = new int[n][n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } } BFS(new Pos(0, 1, 0)); System.out.println(answer); } public static void BFS(Pos pos) { Queue<Pos> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(pos); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Pos poll = queue.poll(); if (poll.x == n-1 && poll.y == n-1) { answer++; continue; } // 오른쪽으로 이동 가능한 경우 : 현 파이프 상태가 가로거나 대각선일 때 if (poll.dir == 0 || poll.dir == 2) { if (isValid(poll.x, poll.y + 1)) { queue.add(new Pos(poll.x, poll.y+1, 0)); } } // 아래쪽으로 이동 가능한 경우 : 현 파이프 상태가 세로거나 대각선일 때 if (poll.dir == 1 || poll.dir == 2) { if (isValid(poll.x + 1, poll.y)) { queue.add(new Pos(poll.x+1, poll.y, 1)); } } // 이전의 상태가 어떻든 대각선 방향은 모두 이동 가능 if (isValid(poll.x + 1, poll.y + 1) && checkAround(poll.x + 1, poll.y + 1)) { queue.add(new Pos(poll.x+1, poll.y + 1, 2)); } } } public static boolean checkAround (int nextX, int nextY) { return map[nextX-1][nextY] == 0 && map[nextX][nextY-1] == 0 && map[nextX][nextY] == 0; } public static boolean isValid(int nextX, int nextY) { return nextX >= 0 && nextX < n && nextY >= 0 && nextY < n && map[nextX][nextY] == 0; } public static class Pos { int x; int y; int dir; Pos (int x, int y, int dir) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.dir = dir; } } }참고로 위 케이스 3개 생각해보면 DP로 푸는게 훨씬 간단하다는 것을 알 수 있다..
DP 배열을 방향까지 저장하기 위해 int[n][n][3] 크기의 3차원 배열로 만들면 된다.import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.StringTokenizer; public class p17070_DP { private static int n; private static int[][] map; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); map = new int[n][n]; int[][][] DP = new int[n][n][3]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } } DP[0][1][0] = 1; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 2; j < n; j++) { if (map[i][j] == 0) { // 해당 좌표에 가로로 오는 법 DP[i][j][0] = DP[i][j-1][0] + DP[i][j-1][2]; // 세로로 오는 법 if (i >= 1) { DP[i][j][1] = DP[i-1][j][1] + DP[i-1][j][2]; // 대각선으로 오는 법 if (map[i-1][j] == 0 && map[i][j-1] == 0) { DP[i][j][2] = DP[i-1][j-1][0] + DP[i-1][j-1][1] + DP[i-1][j-1][2]; } } } } } System.out.println(DP[n-1][n-1][0] + DP[n-1][n-1][1] + DP[n-1][n-1][2]); } }백준 2212
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2212
2212번: 센서
첫째 줄에 센서의 개수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 10,000), 둘째 줄에 집중국의 개수 K(1 ≤ K ≤ 1000)가 주어진다. 셋째 줄에는 N개의 센서의 좌표가 한 개의 정수로 N개 주어진다. 각 좌표 사이에는 빈 칸이 하나 있
www.acmicpc.net
그리디 알고리즘
수학적인(?) 생각이 좀 필요했다.6 2 1 6 9 3 6 7일단 각 센서 위치를 오름차순으로 정렬한 후, 각 센서별로 이웃하는 센서와의 거리차이를 기록한다.
센서 위치 : 1 3 6 6 7 9
각 센서 간 차이 : 2 3 0 1 2 => 3 2 2 1 0 (내림차순)
그리고 이 센서간 차이들 중 가장 큰것부터 (센서 개수 - 1 )만큼 제거하면 된다. 그림이 좀 더 이해가 쉽다.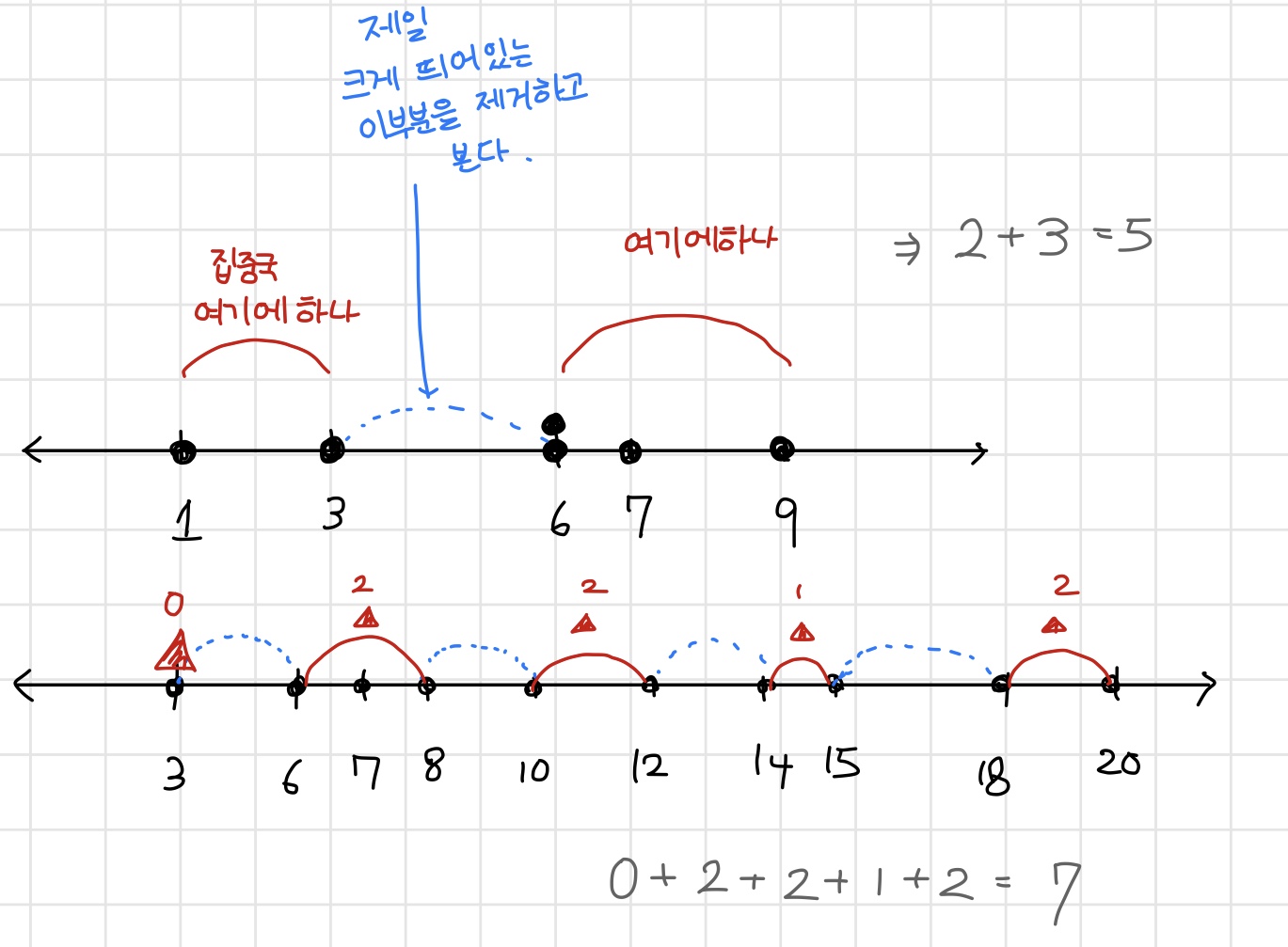
import java.util.*; import java.io.*; public class p2212 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); int spot = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); int answer = 0; ArrayList<Integer> dif = new ArrayList<>(); StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int[] sensor = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { sensor[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } if (spot > n) { System.out.println(answer); return; } Arrays.sort(sensor); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { dif.add(sensor[i] - sensor[i-1]); } Collections.sort(dif, Collections.reverseOrder()); for (int i = spot-1; i < dif.size(); i++) { answer += dif.get(i); } System.out.println(answer); } }백준 12018
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/12018
12018번: Yonsei TOTO
첫째 줄에는 과목 수 n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100)과 주어진 마일리지 m (1 ≤ m ≤ 100)이 주어진다. 각 과목마다 2줄의 입력이 주어지는데 첫째 줄에는 각 과목에 신청한 사람 수 Pi과 과목의 수강인원 Li이 주어
www.acmicpc.net
- 얘도 그리디인데, 조건 몇 개만 잘 보면 된다.
- 무조건 주어진 마일리지 한도 내에서 많이 듣는게 목적이니 수강인원이 차지 않은 과목(cur< limit)은 다 넣기. 최소값인 1만 넣으면 된다
- 수강인원보다 더 신청자가 많다면, 내가 딱 수강인원 커트에 들어가도록 마일리지를 사용하면 된다. 제일 낮은 애 마일리지부터 탐색, 4명이 정원인데 6명신청했다 이러면 3번째로 낮은애 마일리지만큼 사용하면 된다.
import java.util.*; import java.io.*; public class p12018 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int answer = 0; PriorityQueue<Integer> spend = new PriorityQueue<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int cur = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int limit = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); if (cur < limit) { spend.add(1); } else { PriorityQueue<Integer> temp = new PriorityQueue<>(); for (int j = 0; j < cur; j++) { temp.add(Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken())); } if (cur > limit) { for (int j = cur - limit; j > 0; j--) { temp.poll(); } } int min = temp.poll(); spend.add(min); } } while (!spend.isEmpty()) { int poll = spend.poll(); if (m - poll >= 0) { answer++; m -= poll; } if (m <= 0) { break; } } System.out.println(answer); } }백준 14719
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1471914719번: 빗물
첫 번째 줄에는 2차원 세계의 세로 길이 H과 2차원 세계의 가로 길이 W가 주어진다. (1 ≤ H, W ≤ 500) 두 번째 줄에는 블록이 쌓인 높이를 의미하는 0이상 H이하의 정수가 2차원 세계의 맨 왼쪽 위치
www.acmicpc.net
- 찾으려는 index 기준으로 왼쪽, 오른쪽 탐색한다.
- 왼쪽의 max, 오른쪽의 max 비교 후 둘 중 더 작은 값에서 index의 높이를 빼준 것이 고이는 빗물 양
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.*; public class p14719 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int height = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int width = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>(); int[] wall = new int[width]; int answer = 0; st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) { wall[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } for (int i = 1; i < width - 1; i++) { // left part int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(wall, 0, i+1); Arrays.sort(left); // right part int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(wall, i+1, width); Arrays.sort(right); if (wall[i] < right[right.length-1] && wall[i] < left[left.length-1]) { answer += (Math.min(right[right.length-1], left[left.length-1]) - wall[i]); } } System.out.println(answer); } }
'Java > 코딩테스트' 카테고리의 다른 글
백준 15486, 14658 (0) 2023.08.02 백준 1027, 14502 (0) 2023.07.30 코딩테스트 직전 정리 (0) 2023.07.23 백준 1149, 12852, 17135 (0) 2023.07.21 백준 20058, 프로그래머스 - 섬 연결하기, 보석쇼핑 (0) 2023.07.12