Node.js 스터디 6주차
Node.js 교과서 7장 MYSQL
✅ 데이터 베이스란?
- 관련성을 가지며 중복이 없는 데이터들의 집합
- 데이터베이스를 관리하는 시스템 : DBMS
- 관계형 데이터 베이스를 관리하는 시스템 : RDBMS
- 관계형 데이터 베이스 : 데이터가 테이블 형태로 이루어져 있으며, 키와 값이라는 종속성을 관계로 표현하는 데이터베이스를 의미한다. Oracle, MySQL등이 대표적이다.
Create Schema `nodeStudy` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8;
use nodeStudy;
📌 nodeStudy라는 이름의 데이터베이스를 형성하고, 사용하는 데이터베이스를 nodeStudy로 설정한다.
📌 관련 명령어
- CREATE TABLE [데이터베이스명.테이블명] : 테이블 생성 명령어
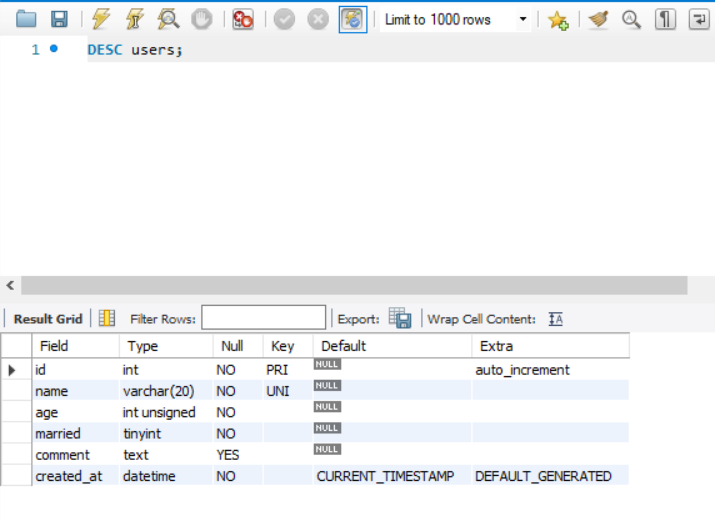
- DESC [테이블명] : 만들어진 테이블 확인
- DROP TABLE [테이블명] : 테이블 제거
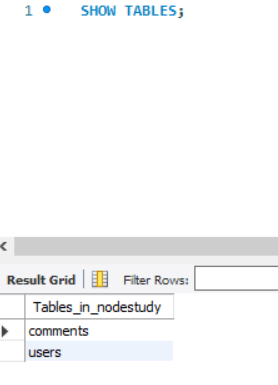
- SHOW TABLES : 생성된 테이블 전체 확인
CREATE TABLE nodeStudy.users (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
age INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
married TINYINT NOT NULL,
comment TEXT NULL,
created_at DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT now(),
PRIMARY KEY(id),
UNIQUE INDEX name_UNIQUE (name ASC))
COMMENT = '사용자 정보'
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET = utf8
ENGINE = InnoDB;✅ SQL 관련 자료형, 옵션 정리
| 칼럼 관련 설정 | 테이블 자체 설정 | |
| 자료형 | 옵션 | COMMENT : 테이블 관한 보충설명, 필수 X |
| INT : 정수형 | NULL : NULL허용 | |
| FLOAT , DOUBLE : 실수형 | NOT NULL : NULL 허용 X | |
| VARCHAR(자릿수) : 가변 길이(0~자료형) | AUTO_INCREMENT : 숫자 자동 증가 | DEFAULT CHARACTER SET : 한글 입력 위해 설정 |
| CHAR(자릿수) : 반드시 길이가 자릿수인 문자열 | UNSIGNED : 음수 저장 X | |
| TEXT : 긴 글 (수백자 넘어가는 경우) | ZEROFILL : 숫자의 자릿수 고정(0001처럼) | |
| TINYINT : 1바이트 정수, boolean처럼 사용 가능 | PRIMARY KEY : 기본 키 설정 | ENGINE : InnoDB |
| DATETIME : 날짜 + 시간 | UNIQUE INDEX : 고유한 값 설정 | |
| DATE : 날짜, TIME : 시간 | DEFAULT : 값이 없다면 기본값 자동 넣음 | |
🔍 InnoDB vs MyISAM
트랜잭션이 많고 대용량 데이터 다룰 경우, 즉 데이터의 변화가 잦은 경우 InnoDB가 효율적
트랜잭션 적고 read작업, 즉 select가 많은 경우 MyISAM이 효율적
사용자의 댓글 저장용 테이블도 만든다.
CREATE TABLE nodeStudy.comments(
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
commenter INT NOT NULL,
comment VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
created_at DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT now(),
PRIMARY KEY(id),
INDEX commenter_idx (commenter ASC),
CONSTRAINT commenter
FOREIGN KEY (commenter)
REFERENCES nodeStudy.users (id)
ON DELETE CASCADE
ON UPDATE CASCADE)
COMMENT = '댓글'
DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4
ENGINE = InnoDB;📌 FOREIGN KEY : 외래키
- 다른 테이블의 기본 키를 저장하는 컬럼
- CONSTRAINT [제약조건명] FOREIGN KEY [컬럼명] REFERENCES [참고하는 컬럼명]
📌 CASCADE 옵션
- ON UPDATE : 수정 되었을 경우, ON DELETE : 삭제 되었을 경우
- CASCADE : 연결된 정보도 함께 수정 OR 삭제 (데이터 불일치를 방지하기 위해)
✅ CRUD 작업하기
📌 CREATE : 데이터를 생성해서 데이터베이스에 넣는 작업
INSERT INTO nodestudy.users (name, age, married, comment) values ('zero', 24, 0, '자기소개1');
INSERT INTO nodestudy.users (name, age, married, comment) values ('nero', 32, 1, '자기소개2');
INSERT INTO nodestudy.comments (commenter, comment) values (1, '안녕하세요 zero의 댓글이에요');
📌 READ : 데이터베이스 내의 데이터를 조회하는 작업
1. 칼럼 전체 조회 (SELECT * )
SELECT * FROM nodestudy.users;
SELECT * FROM nodestudy.comments;

2. 특정 칼럼 조회
SELECT name, married FROM nodestudy.users;
SELECT name, age FROM nodestudy.users WHERE married = 1 AND age > 30;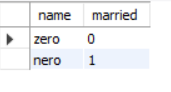

3. 기타 옵션
SELECT id, name FROM nodestudy.users ORDER BY age DESC;
SELECT id, name FROM nodestudy.users ORDER BY age DESC LIMIT 1;
📌 UPDATE : 데이터베이스의 데이터 수정
- UPDATE [테이블명] SET [컬럼명 = 바꿀 값] WHERE [조건] 의 형태
UPDATE nodestudy.users SET comment = '바꿀 내용' WHERE id = 2;
📌 DELETE : 데이터베이스의 데이터 삭제
- DELETE FROM [테이블명] WHERE [조건]
DELETE FROM users WHERE id = 2;
✅ 시퀄라이즈 사용하기
- ORM : 자바스크립트 객체와 데이터베이스의 릴레이션을 매핑해주는 도구
- 사용 이유 : 자바스크립트 구문을 자동으로 sql문으로 바꿔주기 때문
📌 squelize 및 모듈 설치
npm i express morgan nunjucks sequelize sequelize-cli mysql2
npm i -D nodemon📌 models/index.js 수정
const Sequelize = require('sequelize');
const User = require('./user');
const Comment = require('./comment');
const env = process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development';
const config = require('../config/config')[env];
const db = {};
const sequelize = new Sequelize(config.database, config.username, config.password, config);
db.sequelize = sequelize;
db.User = User;
db.Comment = Comment;
User.init(sequelize);
Comment.init(sequelize);
User.associate(db);
Comment.associate(db);
module.exports = db;📌 MYSQL 연결하기
const express = require('express');
const path = require('path');
const morgan = require('morgan');
const nunjucks = require('nunjucks');
const { sequelize } = require('./models'); //models폴더 내 index.js 불러옴.
const app = express();
app.set('port', process.env.PORT || 3001);
app.set('view engine', 'html');
nunjucks.configure('views', {
express : app,
watch : true,
});
sequelize.sync({ force : false }) // sync 메서드 사용 ~ 실행시 mysql과 연동
.then(() => {
console.log('데이터 베이스 연결 성공');
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
});
app.use(morgan('dev'));
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public')));
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended : false }));
app.use((req, res, next) => {
const error = new Error(`${req.method} ${req.url} 라우터가 없습니다. `);
error.status = 404;
next(error);
});
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
res.locals.message = err.message;
res.locals.error = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' ? err : {};
res.status(err.status || 500);
res.render('error');
});
app.listen(app.get('port'), () => {
console.log(app.get('port'), '번 포트에서 대기중');
});📌 config.json 파일 수정 (비밀번호, db 이름 입력)
{
"development": {
"username": "root",
"password": "[root 비밀번호]
"database": "nodestudy",
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"dialect": "mysql"
},
...📌 시퀄라이즈 모델 정의
- ❗ 기본적으로 모델 이름은 단수형, 테이블 이름은 복수형을 사용
- user.js
const Sequelize = require('sequelize');
module.exports = class User extends Sequelize.Model {
static init(sequelize) { // init : 테이블에 대한 설정
return super.init({ // 테이블 칼럼에 대한 설정
name : {
type : Sequelize.STRING(20),
allowNull : false, // null 값 허용 여부
unique : true, // unique(고유값) 여부
},
age : {
type : Sequelize.INTEGER.UNSIGNED,
allowNull : false,
},
married : {
type : Sequelize.BOOLEAN,
allowNull : false,
},
comment : {
type : Sequelize.TEXT,
allowNull : true,
},
created_at : {
type : Sequelize.DATE,
allowNull : false,
defaultValue: Sequelize.NOW, // 기본값
},
}, { // 이 아래부터는 테이블 자체 설정
sequelize, // db.sequelize 객체
timestamps : false, // true일시 createdAt, updatedAt 칼럼 생성
underscored : false, // 캐멀케이스(createdAt)를 스네이크케이스(created_at)로 변경
modelName : 'User', // 모델 이름
tableName : 'users', // 테이블 이름
paranoid : false, // deletedAt 칼럼 생성(지운시간 기록), 후에 복원 가능
charset: 'utf8',
collate : 'utf8_general_ci', // 한글 입력 위한 설정
});
}
static associate(db) {} // 다른 테이블과의 참조 관계
};- comment.js
const Sequelize = require('sequelize');
module.exports = class User extends Sequelize.Model {
static init(sequelize) {
return super.init({
comment : {
type : Sequelize.STRING(100),
allowNull : false,
},
created_at : {
type : Sequelize.DATE,
allowNull : true,
defaultValue: Sequelize.NOW,
},
}, {
sequelize,
timestamps : false,
modelName : 'Comment',
tableName : 'comments',
paranoid : false,
charset: 'utf8mb4',
collate : 'utf8mb4_general_ci',
});
}
static associate(db) {}
};- index.js에 연결 코드 추가
db.User = User;
db.Comment = Comment;
User.init(sequelize);
Comment.init(sequelize);
User.associate(db);
Comment.associate(db);📌 시퀄라이즈와 mysql 차이 간단 정리
| MYSQL | 시퀄라이즈 |
| VARCHAR(100) | STRING(100) |
| INT | INTEGER |
| TINYINT | BOOLEAN |
| DATETIME | DATE |
| INT UNSIGNED | INTEGER.UNSIGNED |
| NOT NULL | allownull : false |
| UNIQUE | unique : true |
| DEFAULT now() | defaultValue : Sequelize.NOW |
✅ 테이블 간의 관계 정의
- 📌 1 : N = hasMany : User 1명은 여러 개의 Comment 생성이 가능
- User.hasMany
db.User.hasMany(db.Comment, { foreignKey : 'commenter', sourceKey : 'id' });- Comment.belongsTo
db.Comment.belongsTo(db.User, { foreignKey : 'commenter', targetKey : 'id' });
- 📌 1 : 1 = hasOne : User 1명은 하나의 Info를 갖는다
db.User.hasOne(db.Info, { foreignKey : 'UserId', sourceKey : 'id' });
db.Info.belongsTo(db.User, { foreignKey : 'UserId', targetKey : 'id' });
- 📌 N : M = belongsToMany : Post는 여러개의 Hashtag 가질 수 있고, Hashtag는 여러개의 Post에 쓰일 수 있음
db.Post.belongsToMany(db.Hashtag, { through : 'PostHashtag' });
db.Hashtag.belongsToMany(db.Post, { through : 'PostHashtag' });✅ 시퀄라이즈 CRUD 쿼리
- 📌 CREATE
INSERT INTO nodestudy.users (name, age, married, comment) values ('zero', 24, 0, '자기소개1');const { User } = require('../models');
User.create({
name : 'zero',
age : 24,
married : false,
comment : '자기소개1',
});
- 📌 READ
SELECT * FROM nodestudy.users;
SELECT * FROM nodestudy.users LIMIT 1;User.findAll({});
User.findOne({});SELECT name, age FROM nodestudy.users WHERE married = 1 AND age > 30;const { Op } = require('sequelize');
const { User } = require('../models');
User.findAll({
attributes : ['name', 'age'],
where : {
married : true,
age : { [Op.gt] : 30 }, // Op.gt : Op객체의 gt 함수, 초과를 의미
},
});
- 📌 UPDATE
UPDATE nodestudy.users SET comment = '바꿀 내용' WHERE id = 2;User.update({
comment : '바꿀 내용',
}, {
where : { id : 2 },
});
- 📌 DELETE
DELETE FROM users WHERE id = 2;User.destory({
where : { id : 2 },
});✅ 시퀄라이즈 관계 쿼리
const user = await User.findOne({
include : [{
model : Comment,
}] // 특정 사용자를 가져오면서 그 사용자의 댓글까지 가져오고 싶은 경우 사용하는 옵션
});
// 혹은 아래처럼 관계 설정시 자동 생성되는 동사+모델이름 형태의 메소드 사용가능
const user = await User.findOne({});
const comments = await user.getComments(); // 조회- ❗ 그 밖에 set(수정), add(생성), remove(삭제)등의 메서드도 지원
const user = await User.findOne({
include : [{
model : Comment,
where : {
id : 1,
},
}]
});
const comments = await user.getComments({
where : {
id : 1,
},
attributes : ['id']
});- 쿼리에도 where, attributes등의 옵션 사용도 가능
const [ result, metadata ] = await sequelize.query('SELECT * from comments');- 직접 SQL 쿼리 사용하는 방법도 있음
✅ 실습 코드 (프론트 코드 생략)
// 사용자 이름을 누르면 댓글 로딩
document.querySelectorAll('#user-list tr').forEach((el) => {
el.addEventListener('click', function() {
const id = el.querySelector('td').textContent;
getComment(id);
});
});
// 사용자 가져오기
async function getUser() {
try {
const res = await axios.get('/users');
const users = res.data;
console.log(users);
const tbody = document.querySelector('#user-list tbody');
tbody.innerHTML = '';
users.map(function (user) {
const row = document.createElement('tr');
row.addEventListener('click', () => {
getCommnet(user.id);
});
let td = document.createElement('td');
td.textContent = user.id;
row.appendChild(td);
td = document.createElement('td');
td.textContent = user.name;
row.appendChild(td);
td = document.createElement('td');
td.textContent = user.age;
row.appendChild(td);
td = document.createElement('td');
td.textContent = user.married ? '기혼' : '미혼';
row.appendChild(td);
tbody.appendChild(row);
})
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
}
// 댓글 가져오기
async function getComment(id) {
try {
const res = await axios.get(`/users/${id}/comments`);
const comments = res.data;
const tbody = document.querySelector('#comment-list tbody');
tbody.innerHTML = '';
comments.map(function (comment) {
const row = document.createElement('tr');
let td = document.createElement('td');
td.textContent = comment.id;
row.appendChild(td);
td = document.createElement('td');
td.textContent = comment.User.name;
row.appendChild(td);
td = document.createElement('td');
td.textContent = comment.comment;
row.appendChild(td);
const edit = document.createElement('button');
edit.textContent = '수정';
edit.addEventListener('click' , async () => {
const newComment = prompt('바꿀 내용을 입력하세요');
if(!newComment) {
return alert('반드시 내용을 입력해야 합니다. ');
}
try {
await axios.patch(`/comments/${comment.id}`, { comment : newComment });
getComment(id);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
});
const remove = document.createElement('button');
remove.textContent = '삭제';
remove.addEventListener('click', async () => {
try {
await axios.delete(`/comments/${comment.id}`);
getComment(id);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
});
td = document.createElement('td');
td.appendChild(edit);
row.appendChild(td);
td = document.createElement('td');
td.appendChild(remove);
row.appendChild(td);
tbody.appendChild(row);
});
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
}
//사용자 등록
document.getElementById('user-form').addEventListener('submit', async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const name = e.target.username.value;
const age = e.target.age.value;
const married = e.target.married.checked;
if(!name) {
return alert('이름을 입력하세요');
}
if(!age) {
return alert('나이를 입력하세요');
}
try {
await axios.post('/users', {name, age, married});
getUser();
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
e.target.username.value = '';
e.target.age.value = '';
e.target.married.checked = false;
});
// 댓글 등록
document.getElementById('comment-form').addEventListener('submit', async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const id = e.target.userid.value;
const comment = e.target.comment.value;
if(!id) {
return alert('아이디를 입력하세요');
}
if(!comment) {
return alert('댓글을 입력하세요');
}
try {
await axios.post('/comments', { id, comment });
getComment(id);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
e.target.userid.value = '';
e.target.comment.value = '';
});
- app.js 연결
const indexRouter = require('./routes');
const usersRouter = require('./routes/users');
const commentsRouter = require('./routes/comments');
.
.
.
app.use('/', indexRouter);
app.use('/users', usersRouter);
app.use('/comments', commentsRouter);
- routes 폴더 생성 및 index.js 파일 작성
const express = require('express');
const User = require('../models/user');
const router = express.Router();
router.get('/', async(req, res, next) => { // '/'로 Get 요청 들어왔을 경우
try {
const users = await User.findAll(); // 모든 유저 찾기
res.render('sequelize', { users }); // users를 렌더링
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
next(err);
}
});
module.exports = router;
- routes/user.js
const express = require('express');
const User = require('../models/user');
const Comment = require('../models/comment');
const router = express.Router();
router.route('/')
.get(async (req, res, next) => { // 사용자 조회 요청(get)
try {
const users = await User.findAll();
res.json(users); // json형식의 데이터 반환
}
catch (err) {
console.error(err);
next(err);
}
})
.post(async (req, res, next) => { // 사용자 등록 요청(post)
try {
const user = await User.create({
name : req.body.name,
age : req.body.age,
married : req.body.married,
});
console.log(user);
res.status(201).json(user);
} catch(err) {
console.error(err);
next(err);
}
});
router.get('/:id/comments' , async(req, res, next) => {
try {
const comments = await Comment.findAll ({
include : {
model : User,
where : { id : req.params.id },
},
});
console.log(comments);
res.json(comments); // 특정 사용자의 댓글들 불러옴
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
next(err);
}
});
module.exports = router;
- routes/comment.js
const express = require('express');
const { User, Comment } = require('../models');
const router = express.Router();
router.post('/', async(req, res, next) => { // 댓글 작성
try {
const comment = await Comment.create({
commenter: req.body.id,
comment : req.body.comment,
});
console.log(comment);
res.status(201).json(comment);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
next(err);
}
});
router.route('/:id')
.patch(async (req, res, next) => { // 댓글 수정
try {
const result = await Comment.update({
comment: req.body.comment,
}, {
where : {id : req.params.id},
});
res.json(result);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
next(err);
}
})
.delete(async(req, res, next) => { // 댓글 삭제
try {
const result = await Comment.destroy({ where : {id : req.params.id } });
res.json(result);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
next(err);
}
});
module.exports = router;
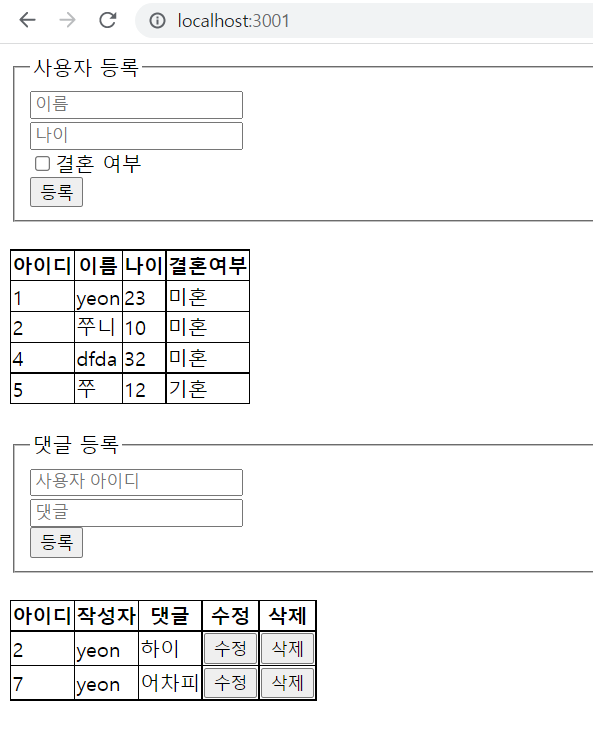
- 실습 화면